Chiropractic, Physical Therapy, Massage & Integrated Services
Find Us On

Request Appointment
Hero Request Form
Appointments Are Available From 9:00 am - 5:30 pm
Offices in Chicago and Lake Forest, IL

Chicago Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
30 South Michigan Avenue
Suite 402
Chicago, IL 60603
Comprehensive Chiropractic Care for Optimal Wellness
At Chicago Chiropractic Center, we're dedicated to providing exceptional chiropractic care and holistic wellness solutions in Chicago and Lake Forest, IL. Since our establishment in 1991, we've been committed to helping patients achieve optimal health through personalized treatment plans and a wide range of innovative therapies.
Whether you're seeking relief from chronic pain, recovering from a sports injury, or simply aiming to improve your overall health, our experienced team is here to guide you on your wellness journey. Contact us today to schedule an appointment.
Your Path to Improved Health and Wellness Starts Here
Choosing Chicago Chiropractic Center means selecting a partner in your health and wellness journey. We stand out with our commitment to personalized care, offering tailored treatment plans that address your unique needs.
By choosing us, you're not just selecting a chiropractor; you're opting for a comprehensive wellness approach that considers your entire body and overall health goals. With locations in both Chicago and Lake Forest, we make quality chiropractic care accessible to a broader community. Contact us today to set up an appointment!
Free Initial Consultations
Emergency Appointments Available
Treat Your Whole Body in One Place
Woman-Owned Practice
Over 30 Years of Experience
We Handle the Insurance Paperwork
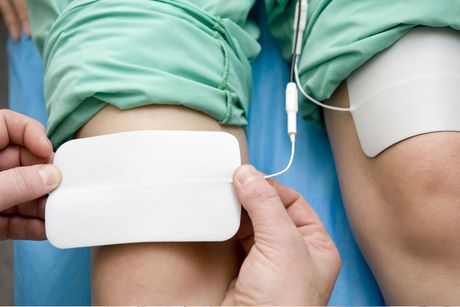
ARP Therapy
ARP (Accelerated Recovery Performance) therapy is an advanced treatment option we offer at Chicago Chiropractic Center. This innovative therapy uses electrical stimulation to target specific muscle groups, promoting faster healing and recovery.

Electrical Stimulation
Electrical stimulation is a versatile treatment modality used in our practice to alleviate pain and promote muscle rehabilitation. This therapy involves the application of mild electrical currents to affected areas, helping to reduce inflammation and accelerate healing.
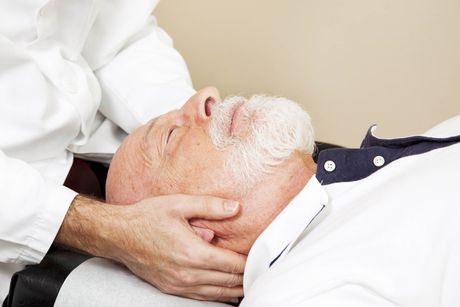
Craniosacral Therapy
Craniosacral therapy is a gentle, hands-on approach that focuses on the craniosacral system, which includes the structures of the central nervous system. This therapy aims to release tensions deep within the body, alleviating pain and dysfunction.

Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care forms the cornerstone of our practice at Chicago Chiropractic Center. Our skilled chiropractors use manual adjustment techniques to correct misalignments in the spine and other joints, promoting proper nervous system function and overall health.
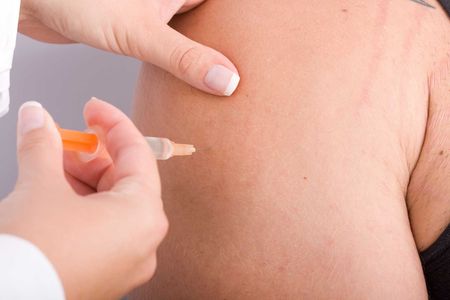
Trigger Point Injections
Chicago Chiropractic Center provides targeted trigger point injection therapies designed to alleviate chronic muscle pain. Our experienced practitioners focus on painful muscle knots that may lead to discomfort and reduced mobility.

Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is an integral part of our holistic approach to wellness at Chicago Chiropractic Center. Our on-site massage therapists offer a variety of techniques to address muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is an advanced treatment method we employ to deliver medication directly through the skin. This non-invasive technique uses a mild electrical current to transport anti-inflammatory medications or pain relievers to specific areas of the body.
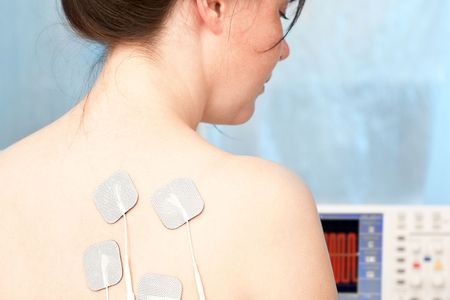
Microcurrent Therapy
Microcurrent therapy is a cutting-edge treatment offered at our center, utilizing low-level electrical currents to stimulate healing at the cellular level. This therapy is effective in reducing pain and inflammation, and promoting tissue repair.
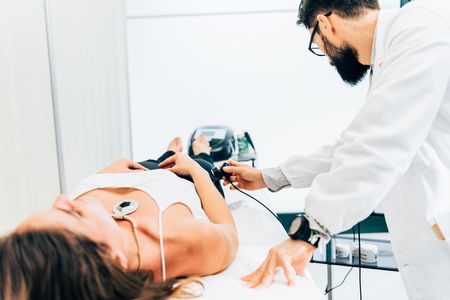
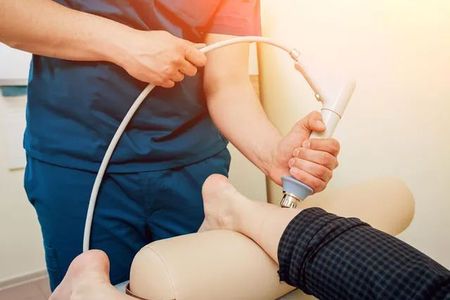
Ultrasound Therapy
Therapeutic ultrasound is a valuable tool in our treatment arsenal at Chicago Chiropractic Center. This non-invasive therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to penetrate deep into soft tissues, promoting healing and reducing pain for the patient.
Here's what our satisfied patients are saying...
At Chicago Chiropractic Center, we take pride in providing exceptional chiropractic and wellness care to our patients. We would be grateful if you could share your thoughts about our practice with others. Your feedback helps us improve and helps others make informed decisions. Please take a moment to leave a review of Chicago Chiropractic Center and let others know what you think.









Share On: